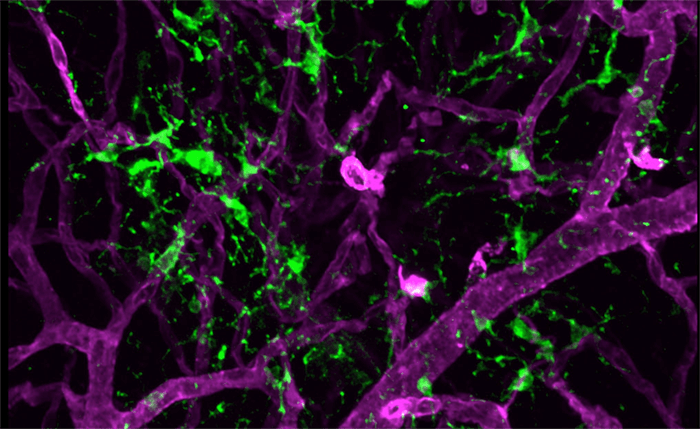
It is fair to say microglia are misunderstood. Best known for being the resident immune cells of the retina, microglia have traditionally been overlooked in favor of other glial cells. But now, a team at Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Boston, USA, has thrown microglia into the spotlight by discovering that they play a protective role in response to a common complication: retinal detachment (RD). “Our results provide clear evidence that microglia protect photoreceptors from cell death in acute RD,” says Kip Connor, senior author on the associated paper. After inducing acute RD in murine retinae, the team found that retinal microglia were rapidly activated in response, migrating to the injured area within 24 hours where they associated with infiltrating macrophages. When microglia were depleted, photoreceptor death increased. The team also discovered that activated microglia cells phagocytosed injured and dying photoreceptors.
“These findings provide the first insight into how microglia respond and function during RD, but our original hypothesis was the polar opposite of what we discovered,” says Connor. “We thought that these cells would contribute to inflammation and cause harm. In actuality, these cells were aiding photoreceptor survival in acute retinal detachment.” Although the current standard of care for RD – surgical reattachment – is highly effective from a physical point of view, in some cases, patients experience permanent vision loss, accompanied by changes in color vision. The difference between a positive and negative outcome all comes down to timing. “Speed is critical,” says Connor. “Studies in both human and animal models have shown that photoreceptor cell death is induced as early as 12 hours after RD, and increased severity and duration of detachment results in a significant decrease in overall visual regeneration.” Early intervention could potentially preserve the photoreceptors, improving the visual acuity of patients that undergo both early and late stage reattachment procedures. But do microglial cells present a potential solution? “Our findings begin to identify a new role of microglia, which appear to perform multiple functions in response to retinal injury,” says Connor. “Our hope is that future studies will allow the development of specific therapeutics that enhance microglial function, resulting in greater visual outcomes and quality of life for patients suffering from sight-threatening diseases.”
References
- Y Okunuki et al., “Microglia inhibit photoreceptor cell death and regulate immune cell infiltration in response to retinal detachment”, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, [Epub ahead of print] (2018). PMID: 29915052.
