Sometimes you have to sedate patients to measure IOP – or take IOP readings in patients who are sedated. The question has always been: do anesthetic agents alter IOP readings? If so, does one agent affect IOP more than another?
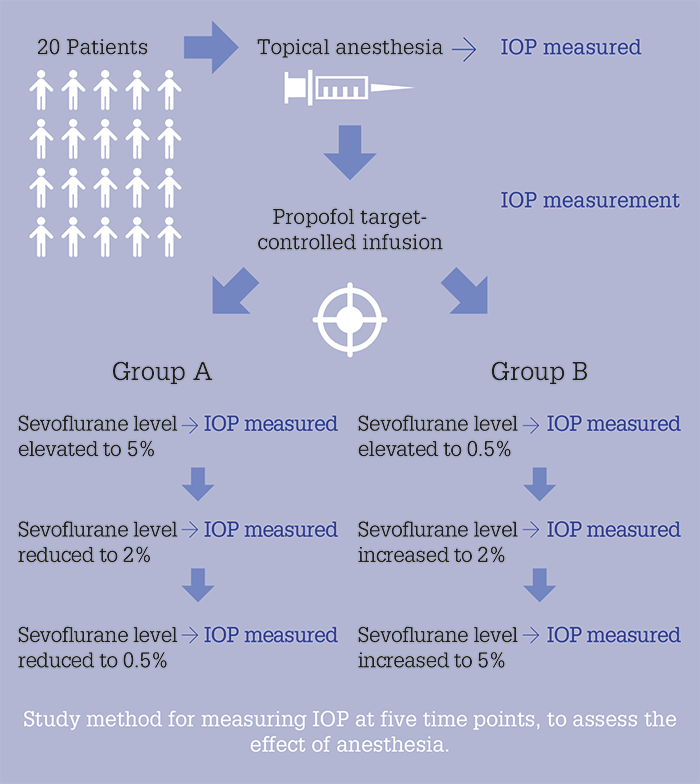
A group from the Tel-Aviv Medical Center decided to find out. They measured the IOP of 20 adult patients undergoing extraocular ophthalmic surgery at five key timepoints of the general anesthesia process: after topical anesthesia, but before the induction of general anesthesia; after the induction using propofol target-controlled infusion, and under the end-tidal concentrations of sevoflurane (0.5%, 2%, and 5%), either in a decreasing (Group A) or an increasing (Group B) concentration order (see Infographic). The result? IOP measurements taken under sedation were not significantly different from the ones taken when patients were awake, suggesting that (in adults at least) these anesthetics can potentially be used without skewing IOP measurements (1).
Study method for measuring IOP at five time points, to assess the effect of anesthesia.
References
- S Kanjlia et al., “Absence of visual experience modifies the neural basis of numerical thinking”, Proc Natl Acad Sci, [Epub ahead of print] (2016). PMID: 27638209.
