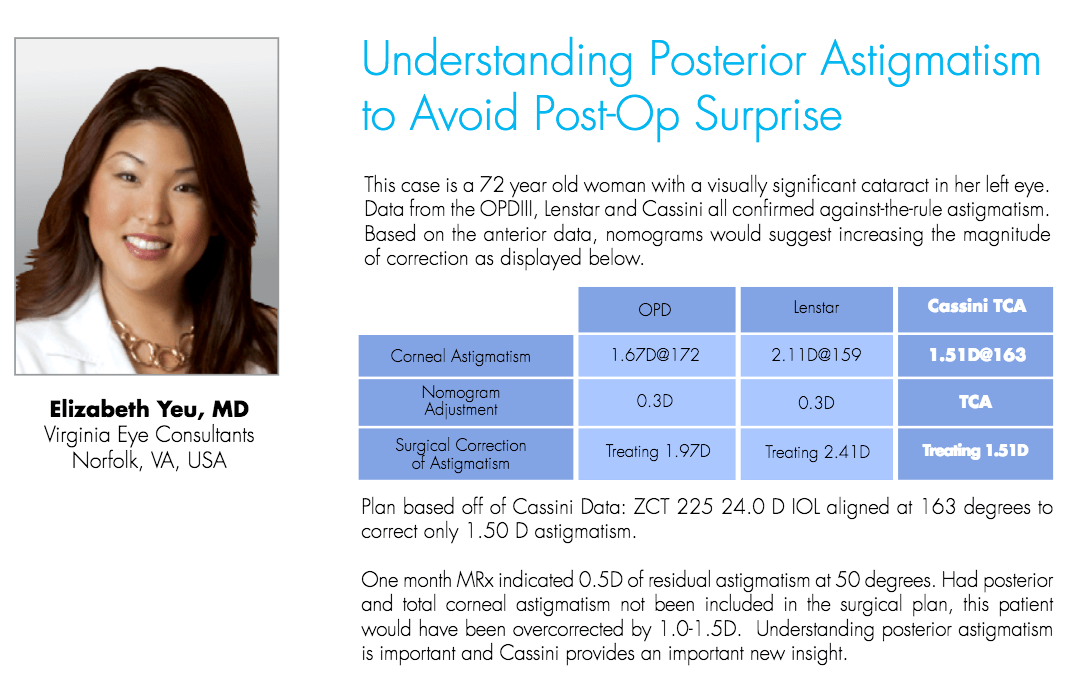
Clinical Case Example: Studies have demonstrated that posterior corneal astigmatism could be a factor in generating unexpected postoperative outcomes. Research has shown that selecting toric IOLs based on anterior corneal measurements could lead to over-correction in eyes that have with-the-rule astigmatism (vertical steep axis) and under-correction in eyes that have against-the-rule astigmatism (horizontal steep axis). In addition, there seems to be a large variety in the relationship between anterior and posterior astigmatism in pre-cataract populations of patients. Keeping this challenge in mind, Cassini has worked closely with many key-opinion leading physicians to help develop a solution. Cassini’s new Total Corneal Astigmatism functionality uses patented second Purkinje reflection-based analysis of the posterior cornea. Cassini posterior and anterior data is calculated to provide surgeons with the total corneal power, as well as steep axis and magnitude of astigmatism. This means that patients undergoing cataract surgery benefits from actual measurements of the Total Corneal Astigmatism (TCA) rather than using a generic nomogram. Cassini provides the data that enables cataract surgeons to create a unique, personalized surgical plan for each patient individually, without ignoring the posterior corneal astigmatism. The following case example provides insight in how Cassini TCA has helped Elizabeth Yeu, MD - Viginia Eye Consultants - to avoid a post-operative surprise:
Read the full Clinical Review here
Cassini Total Corneal Astigmatism helps cataract surgeons to better understand corneal properties in order to improve outcomes and increase premium patient volume. Cassini offers a full suite of examinations required for toric and multifocal IOL implantation. This includes corneal topography, mesopic and photopic pupillometry as well as full color photography for diagnostic purpose. The technology employs red, green and yellow LEDs that are each positioned in a unique relationship to four of its neighbors, giving each one a ’gps-like’ coordinate. Cassini uses the ray- tracing principle to measure the relative position of each point, using the three different colors as ‘triangulation’ points. www.cassinitca.com http://i-optics.com/library/#videos

